The high penetration of distributed power sources into the power system, especially power sources using popular renewable energy sources such as solar panels and wind turbines, is characterized by unstable or intermittent output power due to continuous changes in solar radiation and wind fluctuations, causing major impacts on power quality. In addition, it changes the structure of the power system from the traditional radial structure with a single power supply to a multi-source structure. This change leads to changes in the short-circuit current of the system when a fault occurs due to the short-circuit current contribution from distributed power sources and the short-circuit current contribution from the grid power source is also changed depending on the location and capacity of the distributed power sources connected to the system.
♦ The impacts of distributed generation on power quality and protection equipment coordination of the power system include:
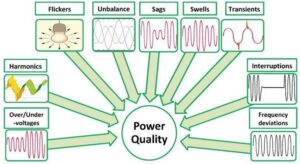
– Voltage transients
– Voltage flicker
– Short-term voltage dips/short-term voltage surges
– Long-term voltage dips/long-term voltage surges
– Voltage imbalances
– Harmonics
– Frequency deviations
– Protection device mismatches
– Protection range reductions
– Changes in protective device tripping sequence
– Changes in fault clearance time
– Misoperations
In addition, the reverse power flow to the grid of distributed power sources causes local heating, increases power loss for electrical equipment, especially distribution transformers, and affects the directional protection system.
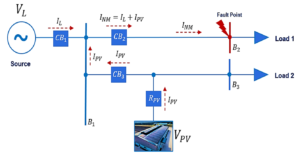
♦ When analyzing the impact of distributed power sources on the power system, information is provided to determine:
– The maximum capacity of the distributed power source that can be connected to the existing power system and the installation location.
– Determine the level of voltage and harmonic abnormalities to propose improvement solutions and select appropriate equipment.
– Provide information and setting points for overcurrent, overload, low voltage, overvoltage protection devices, etc.
– Provide information to determine appropriate switching equipment, arc energy and personal protective equipment.
♦ Applicable standards:
– IEEE 399: Standard for the Analysis of Industrial and Commercial Electrical Systems.
– IEEE 1547: Standard for the Connection of Distributed Generation Sources to the Grid
– IEEE 242: Standard for Coordination of Protective Devices
– IEEE 1584: Standard for Arc Flash Analysis
– IEEE 519: Standard for Power Quality

